Please be aware that Ceros SDK plugins are non-native tools and are provided "as is". As such, we cannot guarantee that plugin functionality will work as intended across all implementation instances.
Add and Control Sounds
We thought it would be fun, and in some cases, pretty useful, if you could integrate sounds and music into your Ceros experiences. Not only does this SDK plugin allow for that, but it also allows you to control your sound files with play/pause buttons, toggles, loops, resets, muting, and other various event triggers. You can also use this plugin to integrate a live stream into your Ceros experience. Import the demo experience below to your Ceros account to explore a finished audio piece, or follow the steps below to set up audio controls on your own.
Click here to import demo experience
Click here to view a recorded webinar that overviews this plugin!
How We Did It
The first thing we did was to devise a naming convention for SDK Tags that would allow us to expose as much functionality from the Howler.js Web Audio library as possible. We then used the Ceros SDK to track integrations with objects whose tags followed the naming convention and to trigger the appropriate audio effects.
What You’ll Need
Custom HTML code snippet
One of more audio files (e.g. mp3, .ogg, .mp4, .webm)
A server to host your audio on (e.g. s3, FTP, Dropbox, Sharefile Box, etc)
A Ceros experience
How to Implement
Step 1: Add the Custom HTML
Copy the SDK script below and paste it into the Custom HTML field within the Settings panel in the Studio. Press OK to finish and close the panel.
<script id="ceros-audio-plugin" src="//labs.ceros.com/sdk-plugins/audio-v5/audio.js" soundTag="playsound"></script>Step 2: Choosing a File Type
Not all audio codecs have full browser support. To view a complete list of codecs with full browser support, click here. We recommend using MP3 files for the best balance of small file size and high quality, however, you can use any of the following:
MP3
MP4
OGG
WEBM
Step 3: Hosting Sound Files
In order for a sound file to be played, it must be hosted on an external server. We’ve attached a demo sound file here if you would like something to test.
If you have your own server that can host files (e.g. s3 or FTP), make sure that it has Cross-Origin Requests (CORS) enabled and is publicly accessible, i.e., not behind a login – anyone should be able to access the file.
If your company has a website, that means there is a web server where your audio file could be hosted. You may need to reach out to your IT team to get this done if you are not able to upload to the server yourself.
Step 4: Adding Sounds to Your Experience

To add a sound file to your experience, you must attach the audio file's URL to the payload section of an icon, image, or text box in the Ceros Studio.
Steps to add an audio file:
1. Find the object you want to attach the sound file to. We recommend placing a sound icon outside the canvas to make it easy to locate.
2. With the object selected, open the SDK Panel and, within the Enter Tag field beneath the SDK ID of the object, type in the tag playsound and press Enter/Return to add it to the object.
3. Add an additional tag of name:unique-name and substitute “unique-name” with a name of your choosing.
4. Paste the URL to the sound file in the Enter Payload section. Ensure there are no extra spaces before or after the URL.
Step 5: Adding Click Events to Trigger a Sound

Sound events are the drivers of the extension and are what give users control over the sounds in an experience. In order for users to interact with your sounds, events must be added to a triggering object.
Steps to add a click event:
1. Create or find the object you would like to add a click event to. We recommend using Hotspots to make it easier to locate in your Layers panel.
2. With the Hotspot or object selected, open the SDK Panel. In the Enter Tag field beneath the object's SDK ID, add a sound-click tag. This tells the experience to listen for click events on this object.
3. Add an additional tag for the event you would like to fire when the Hotspot or object is clicked, such as event:play. We’ve listed all of the possible events below.
4. Finally, identify the sound file you would like to trigger by adding a target:unique-name tag (with "unique-name" being the name you created for your sound object in Step 4).
Please note: Since the Hotspots created for the Audio SDK may only trigger SDK commands, Click and/or Hover events are NOT sent to Ceros Analytics, Google Analytics, or Google Tag Manager. To work around this, there would need to be a Click and/or Hover interaction added to the Hotspot. It can be anything, i.e., toggling the visibility of a shape that exists off the canvas.
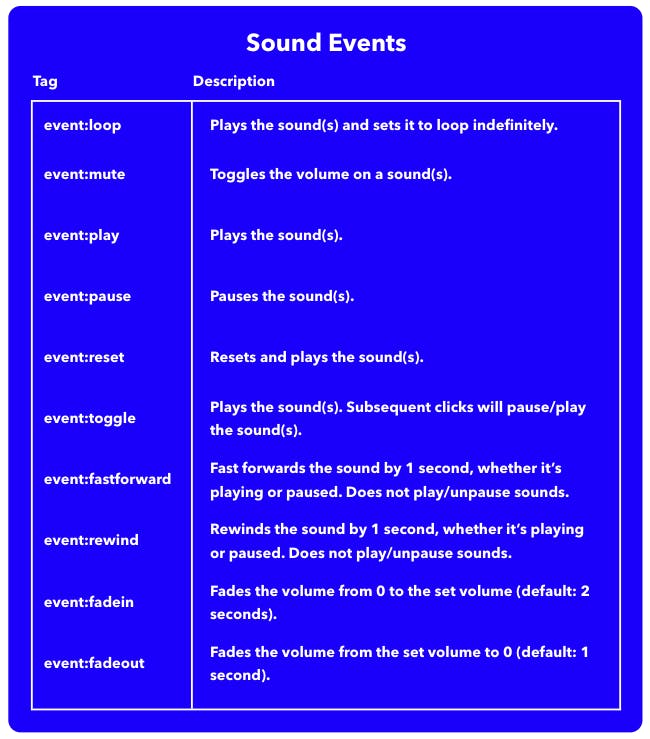
Global events: all events can be applied globally to every sound in the experience. In order to do so, change the event in the event tag to eventall (example: eventall:play).
Optional: Adding Streams to Your Experience
1. Follow the above steps for adding a typical audio file, making sure to add the URL of the source of the stream to the Payload.
2. Add the tag stream:true to the object's tags.
3. Make sure an event is attached, event:toggle is recommended for streams.
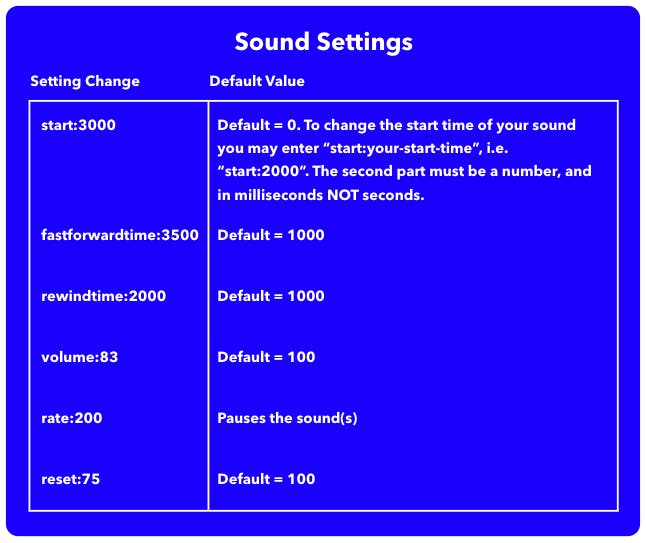
Optional: Sound Settings
If you would like to really fine-tune your sound and/or event settings, much can be done using tags alone. This section will tell you which settings you can change through tags and what those changes do.
WARNING: changing these settings may cause unexpected behavior.
Settings can be changed using the format: setting:value.